
Digital dashboards that help you identify deviations and make the right decisions.

Capture your deviations and turn them into improvements

Continuous improvement, Kaizen boards, PDCA and other tools.

All your team’s tasks, neatly organized in one weekly view.
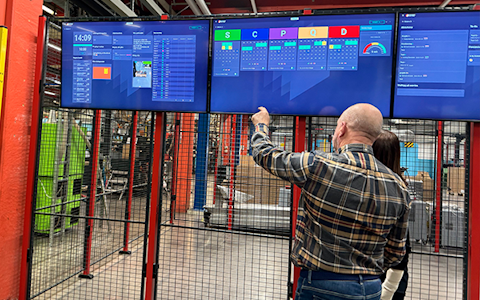
Improve key performance indicators within your specific focus areas with our SQCDP board.

Use the PDCA cycle as a tool to improve both quality and processes

Digital tools for 5S work, recurring audits, and a well-organized workplace.

Visualize KPIs and communicate effectively throughout the entire organization.

Basic project management and activity boards.

Kanban is a powerful method for visualizing, managing, and optimizing workflows.

Digital dashboards for takt time flow with takt time counter and stop time log.

Digital visitor registration provides full control over all planned and executed visits to your business.
Curious about what Lean Production really is and how it can help streamline work processes while cutting waste? In this article, we explore the key methods and tools that make it possible.

Lean was originally developed by the Japanese car manufacturer Toyota and has since been embraced by an increasing number of manufacturing industries. The method is based on a philosophy that focuses on reducing waste and creating clear, efficient ways of working.
As a production method, Lean is used to increase efficiency by reducing waste and improving productivity. The goal is to create greater value for customers using fewer resources, while ensuring that work is characterized by clear communication, collaboration, and high quality. Central to Lean is also a culture of continuous improvement, where constant small changes lead to major results over time.
According to the Lean model, there are seven types of waste that should be avoided:
Traditional whiteboards are still widely used in the manufacturing industry. However, despite their simplicity, this method is time-consuming and makes it difficult to share the right information, at the right time, with the right person. The result is often similar to the telephone game, what is said at the beginning rarely matches what reaches the final recipient.
Digital Lean offers a smarter way of working. Information is stored in the cloud and presented visually and in an easily accessible format, giving both employees and management the same overview. Processes and issues can be monitored in real time, problems are identified immediately, and deviations are addressed quickly, saving time and reducing the risk of misunderstandings.
Key Lean tools
Lean offers many tools for structuring work, monitoring processes, and driving improvements. Below are five important tools, all of which can be used in Boards on Fire’s digital solution for daily management:
With digital tools, it becomes easier to track key metrics in real time and communicate effectively. Boards on Fire gathers all critical information in one place and visualizes it through clear dashboards, charts, and KPIs. This gives employees a quick overview of production and clearly shows what needs to be done, when, and by whom.
For many organizations using Boards on Fire, this has led to increased employee engagement, which in turn improves both efficiency and quality.
Benefits of using Boards on Fire as a Lean tool:
Curious about how our customers use Boards on Fire? Explore our customer case studies for concrete examples.

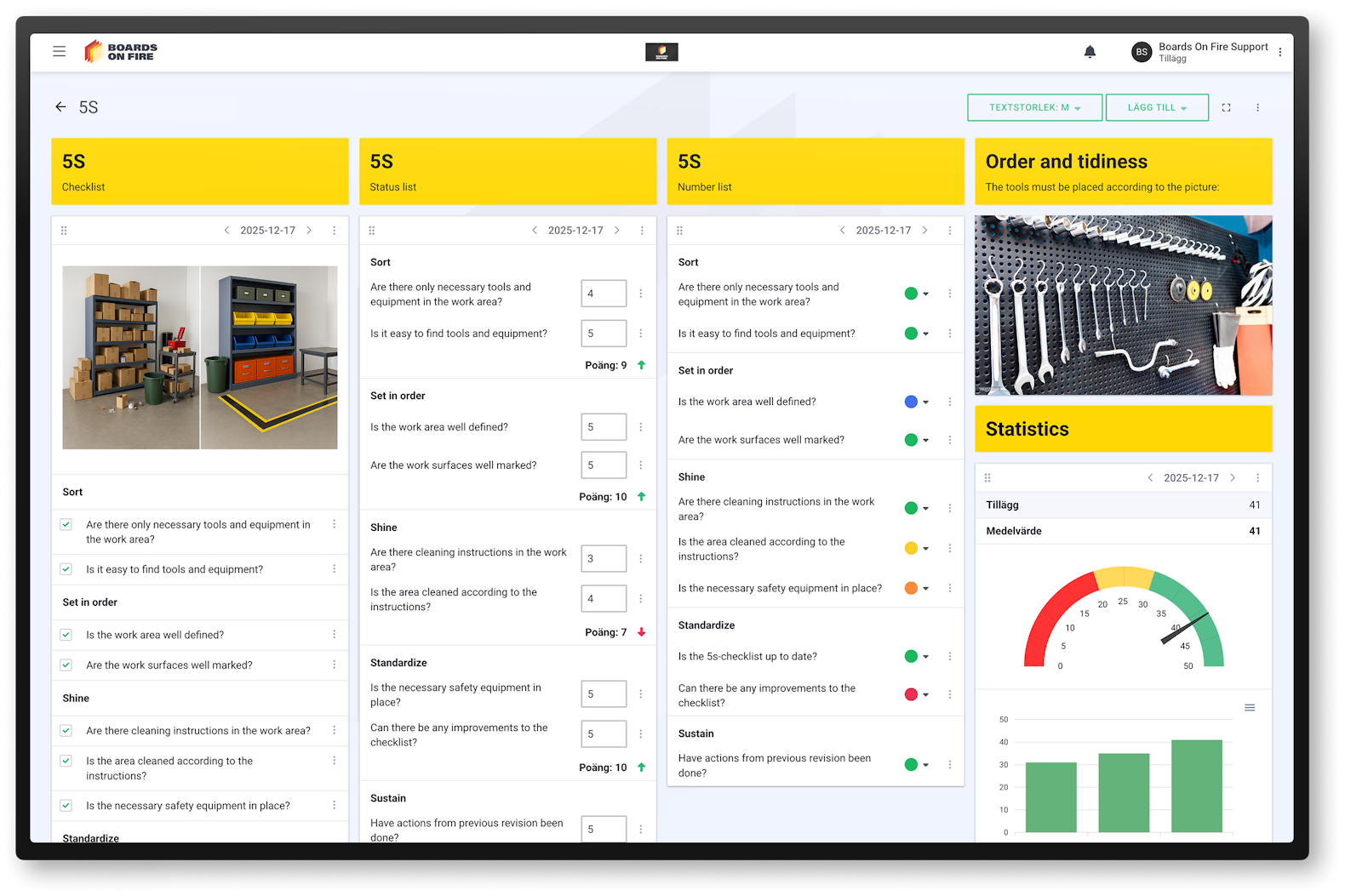
5S is a method aimed at creating a well-organized and efficient workplace. By introducing shared standards for how items should be organized, it becomes easier to quickly find what is needed. This reduces the risk of wasted time and minimizes negative impacts on the factory or workflow.
The five steps of 5S:
With Boards on Fire, you can create customized checklists to carry out regular 5S audits and easily track progress. The system provides clear data for analyzing results, discussing improvement opportunities, and continuously developing work processes.
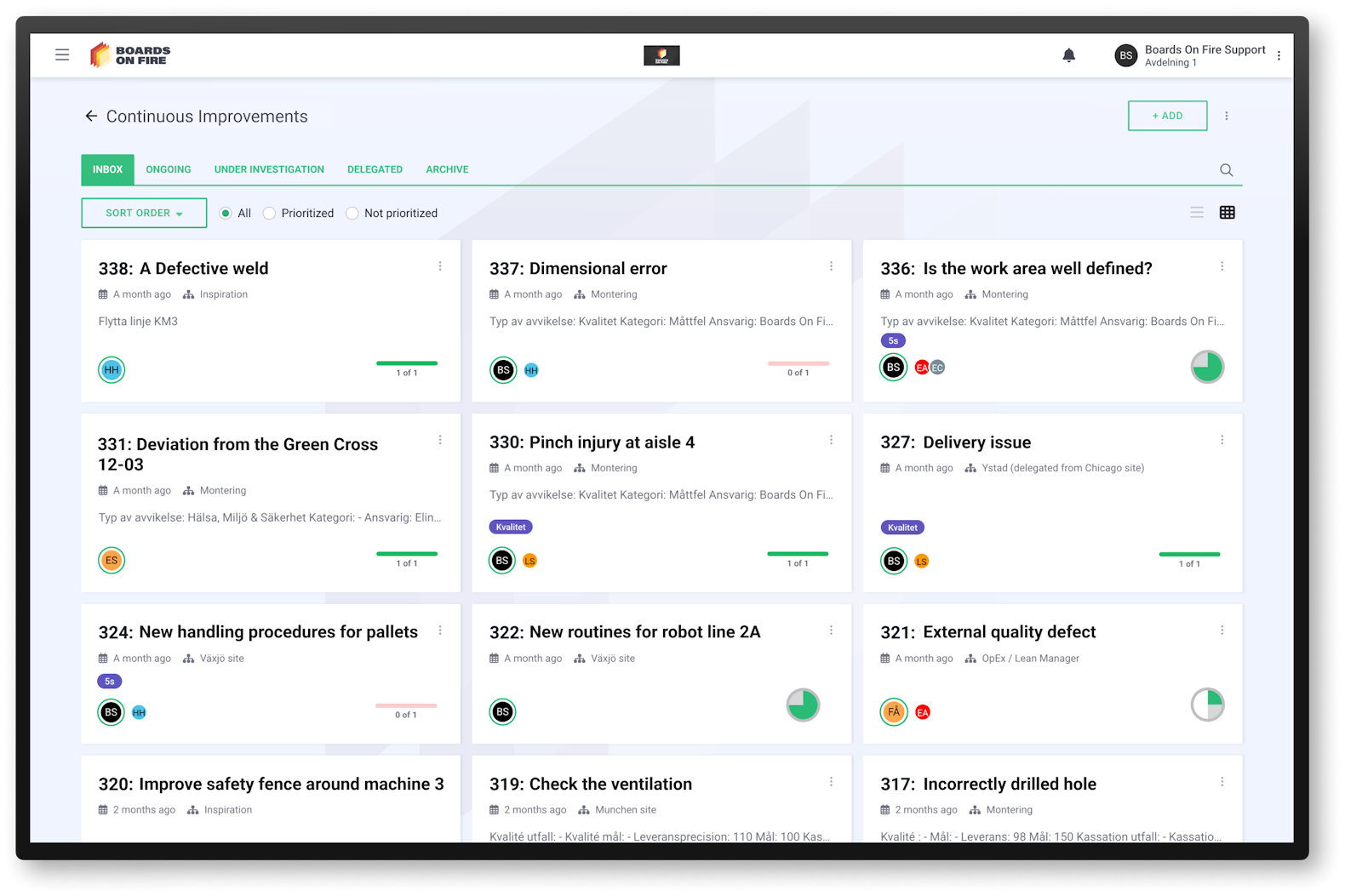
Kaizen is a Japanese philosophy and working method that means “continuous improvement.” The method originated in Japanese industry and is now a central part of the Lean philosophy. The core idea is that improvements happen continuously through many small steps in daily work. All employees contribute by noticing problems and suggesting improvements.
The goal is to reduce waste, improve quality, and increase efficiency. Over time, these small improvements lead to significant and sustainable results. With digital tools, improvement work can be structured, tracked, and made more transparent, making Kaizen a natural part of daily operations.
Gemba Walks are one of the most powerful tools for understanding the current state of operations, identifying waste, and creating opportunities for learning and improvement. The method involves managers and employees visiting the place where value is created (gemba = “the real place” in Japanese), such as the production floor. The focus is on observing, understanding, and learning from daily work rather than controlling, judging, or pointing out faults.
Gemba Walks can be conducted in various ways. The most common is using checklists, often on whiteboards or paper. Regardless of the format, the goal is the same: to create an understanding of how work is actually performed and to drive improvements.
With Boards on Fire’s digital solution for daily management, the impact of Gemba Walks is further enhanced. Walks can be planned, executed, and followed up directly via mobile, tablet, or computer, without losing presence on the floor. The system also allows observations to be documented in real time, results analyzed, recurring problems identified, and clearer improvement plans created. In this way, Gemba Walks become not just a tool for observation, but a practical support for the continuous development of both processes and employee learning.

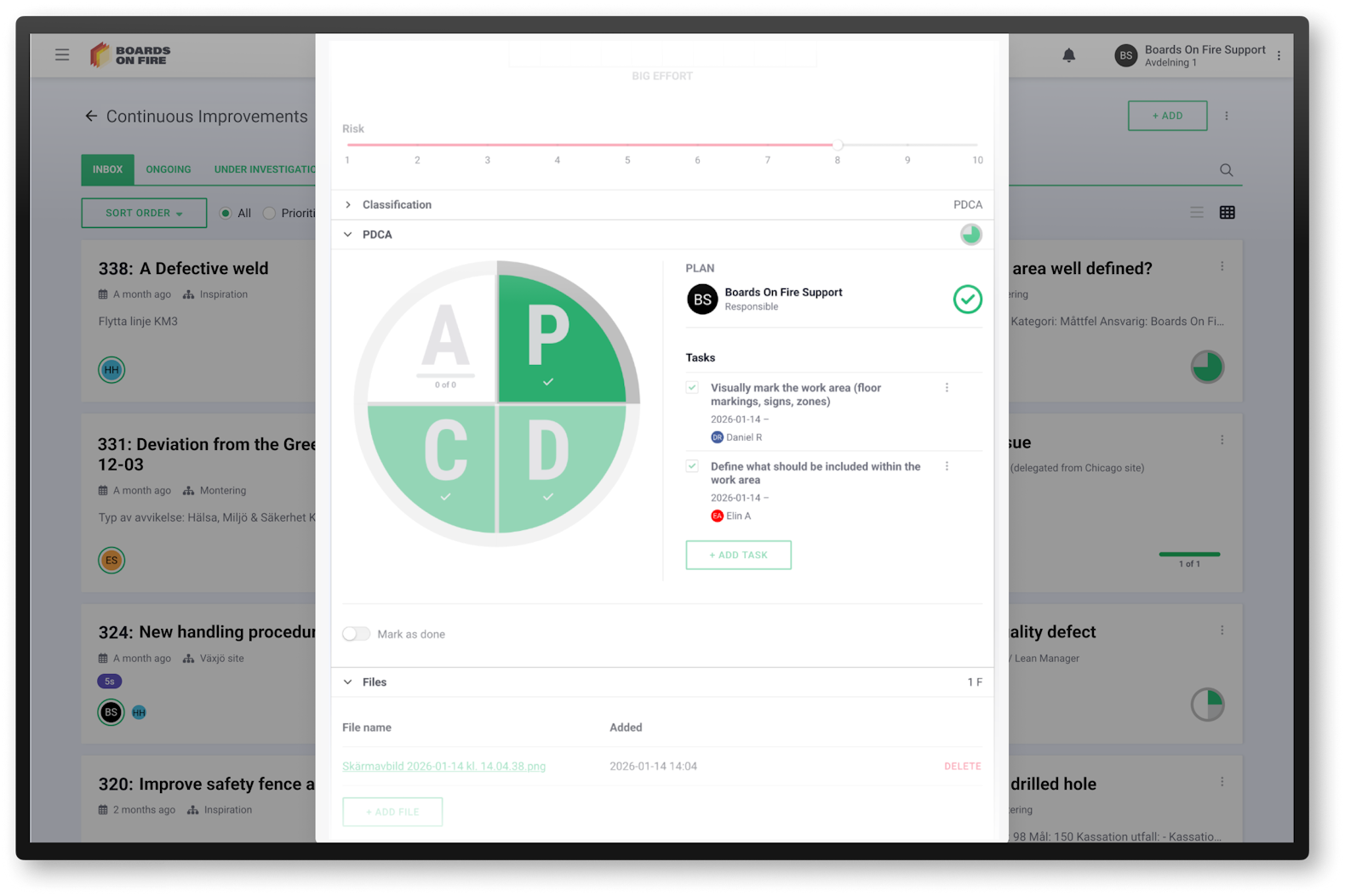
PDCA is a four-step method for the continuous improvement of processes, products, and ways of working. The method helps you identify problems, test solutions, and improve results step by step.
The four steps of PDCA:
With Boards on Fire, you can use PDCA digitally for projects, improvement initiatives, and change management. You can create sub-tasks, delegate responsibilities, track progress, and visualize results for the entire team—all in one place, making improvement work clearer and more efficient.
 |
 |
Happens at Boards on Fire
Free web demo